Mercedes Benz Unveils Solar Paint: Providing 12,000 km Range Per Year for EVs
LienApr 25, 2025, 04:47 PM
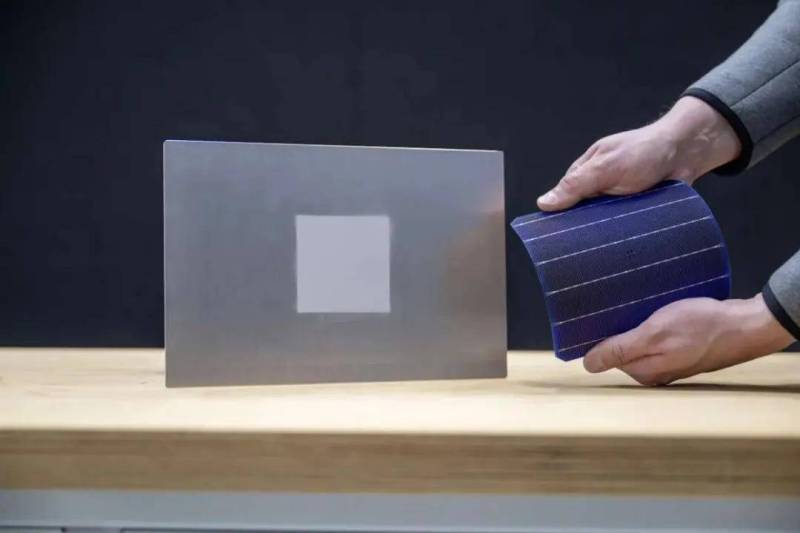

【PCauto】Mercedes-Benz has recently shown a solar paint technology that can utilize sunlight to charge electric vehicles.
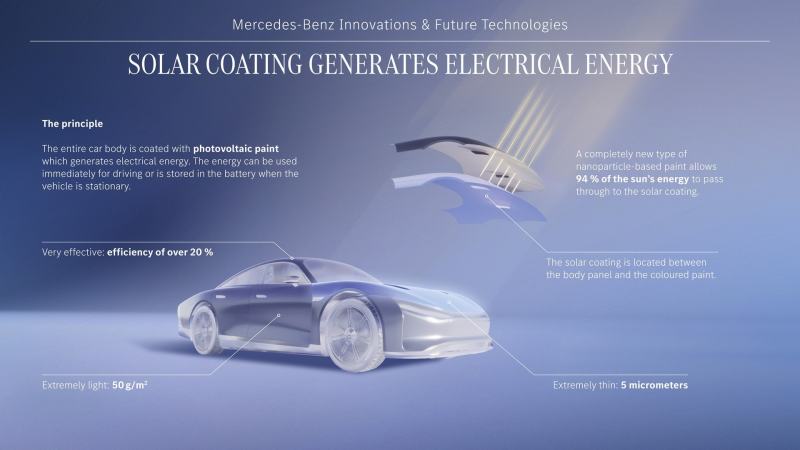
Mercedes’ solar paint is based on nanoparticle technology, with its core working mechanism relying on the photoelectric effect to convert light energy into electrical energy.
When photons from light strike the paint surface, the semiconductor nanoparticles (quantum dots) contained in the coating absorb the photon energy and transfer it to electrons, causing the energized electrons to move and generate an electric current.
The electric current can be effectively directed to the electric vehicle’s electrical system to power various components, or even charge the battery directly.
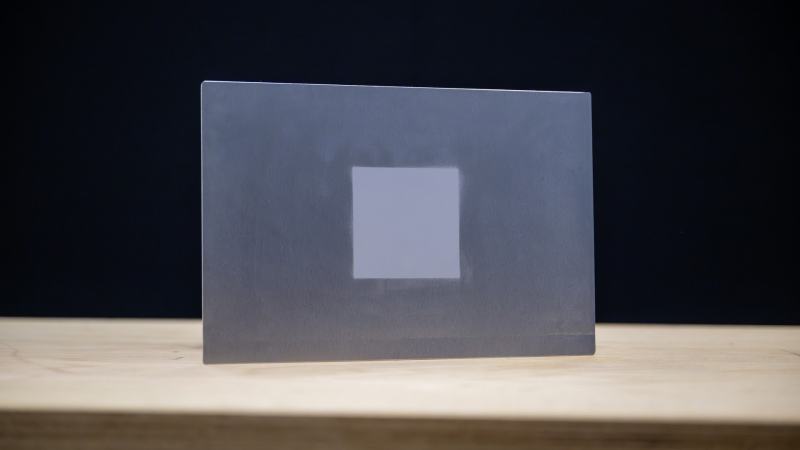
The paint itself possesses several remarkable advantages.
First, the coating is extremely thin at just 5 microns – about one-tenth the diameter of a human hair – and weighs only 50 grams per square meter. This ultra-light property means it adds almost no extra weight when applied to a vehicle body, thus having no negative impact on handling or energy consumption.
Second, the paint offers great flexibility in color selection and can be tinted to any shade according to consumer preferences. However, it’s worth noting that color choice affects the paint’s energy capture efficiency in certain degree, with darker colors generally performing better at capturing solar energy.
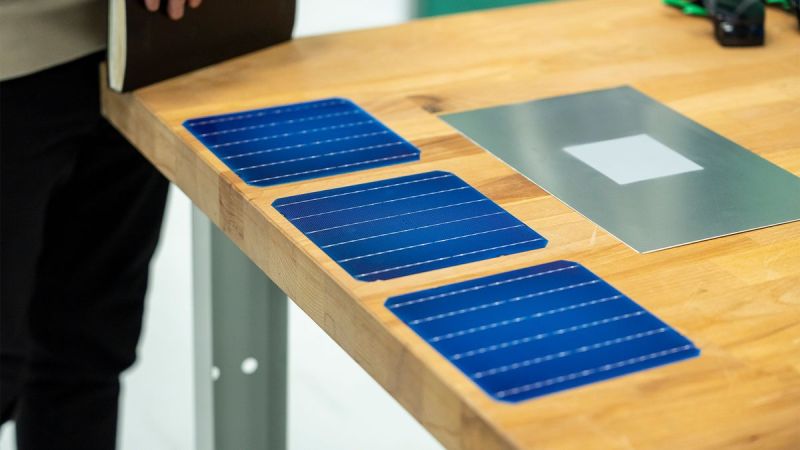

Furthermore, the paint is covered with a special nanoparticle-based coating that serves dual purposes: it allows 94% of sunlight to pass through to the photovoltaic layer beneath for energy conversion, while also acting as a durable shield against scratches, bird droppings, dust and other external factors that could damage the photovoltaic layer, significantly extending the coating’s lifespan and performance stability.
Additionally, this solar paint adopts only non-toxic and readily available materials in its composition, containing no rare earth elements or silicon. This not only reduces its potential harm to the environment but also provides the paint with significant cost advantages, laying a solid foundation for future large-scale commercial applications.
In practical application, Mercedes’ solar paint has demonstrated surprisingly impressive range-extending capabilities. Taking the mid-size SUV GLE-Class as an example, its body surface area measures approximately 11 square meters.
Under ideal lighting conditions, such as in sunny Los Angeles, the electricity generated by this paint can meet the vehicle’s daily driving needs of about 56 kilometers. Calculated annually, the solar-converted electricity could support approximately 20,116 kilometers of driving.
Even in cities with relatively less sunshine, like Stuttgart, Germany, it could still provide around 12,000 kilometers of additional range per year.

This means that in many cases, the energy absorbed and converted by the solar paint alone could satisfy a significant portion of daily travel requirements, greatly reducing reliance on traditional charging methods.
Beyond substantially increasing range, this technology has broader significance. From an environmental perspective, it further advances the automotive industry toward sustainable development. By utilizing clean solar energy to power vehicles, it reduces carbon emissions from conventional power generation, helping reduce global climate change pressures.
From an energy utilization point, vehicles can continuously generate electricity whether parked or in motion. This on-the-go energy capturing method significantly improves energy efficiency. Moreover, excess electricity generated could even be returned to homeowners’ grids through bidirectional charging technology, enabling flexible energy distribution and reuse.

However, despite the promising prospects of Mercedes’ solar paint technology, it currently remains in the research phase with a certain room for be mature before achieving large-scale commercial application.
One of Mercedes’ key prio